Operations on Signals#
This section describes the operations that can be performed on signals.
See also
Processing Signals for more information on signal processing features, or Analysis features on Signals for information on analysis features on signals.
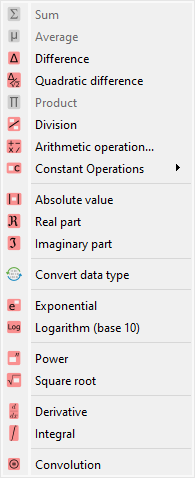
Screenshot of the “Operations” menu.#
When the “Signal Panel” is selected, the menus and toolbars are updated to provide signal-related actions.
The “Operations” menu allows you to perform various operations on the selected signals, such as arithmetic operations, peak detection, or convolution.
Operations with a constant#
Create a new signal which is the result of a constant operation on each selected signal:
Operation |
Description |
|---|---|
|
\(y_{k} = y_{k-1} + c\) |
|
\(y_{k} = y_{k-1} - c\) |
|
\(y_{k} = y_{k-1} \times c\) |
|
\(y_{k} = \dfrac{y_{k-1}}{c}\) |
Basic arithmetic operations#
Operation |
Description |
|---|---|
|
\(y_{M} = \sum_{k=0}^{M-1}{y_{k}}\) |
|
\(y_{2} = y_{1} - y_{0}\) |
|
\(y_{M} = \prod_{k=0}^{M-1}{y_{k}}\) |
|
\(y_{2} = \dfrac{y_{1}}{y_{0}}\) |
|
\(y_{2} = \dfrac{1}{y_{1}}\) |
|
\(y_{2} = \exp(y_{1})\) |
|
\(y_{2} = \log_{10}(y_{1})\) |
Convolution and Deconvolution#
Operation |
Implementation |
|---|---|
|
Based on scipy.signal.convolve |
|
Frequency domain deconvolution |
Absolute value and complex signal operations#
Operation |
Description |
|---|---|
|
\(y_{k} = |y_{k-1}|\) |
|
|
|
Consider current signal as the module and allow to select a signal representing the phase to merge them in a complex signal
|
|
\(y_{k} = \Re(y_{k-1})\) |
|
\(y_{k} = \Im(y_{k-1})\) |
|
Consider current signal as the real part and allow to select a signal representing the imaginary part to merge them in a complex signal |
Data type conversion#
The “Convert data type” action allows you to convert the data type
of the selected signals.
Note
Data type conversion relies on numpy.ndarray.astype() function with
the default parameters (casting=’unsafe’).
Statistics between signals#
Create a new signal which is the result of a statistical operation on each point of the selected signals:
Operation |
Description |
|---|---|
|
\(y_{M} = \dfrac{1}{M}\sum_{k=0}^{M-1}{y_{k}}\) |
|
\(y_{M} = \sqrt{\dfrac{1}{M}\sum_{k=0}^{M-1}{(y_{k} - \bar{y})^{2}}}\) |
Other mathematical functions#
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
|
\(y_{k} = y_{k}^{n}\) |
|
\(y_{k} = \sqrt{y_{k}}\) |
|
Based on numpy.gradient |
|
Based on scipy.integrate.cumulative_trapezoid |
|
Create a 2D image by assembling selected 1D signals as rows or columns, with optional normalization. |