Manipulate metadata and annotations#
This section describes how to manipulate metadata and annotations in DataLab.
Signal metadata contains various information about the signal or its representation, such as view settings, Regions Of Interest (ROIs), processing chain history, analysis results, and any other information that you may have added to the metadata of a signal (or that comes from the signal file itself).
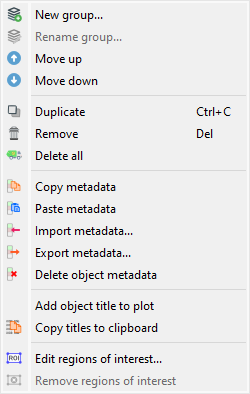
Screenshot of the “Edit” menu.#
The “Edit” menu allows you to perform classic editing operations on the current signal or group of signals (create/rename group, move up/down, delete signal/group of signals, etc.).
As detailed below, it also allows you to:
Navigate and utilize the processing chain history through actions like “Recompute” and “Select source objects”.
Manipulate metadata and annotations associated with the current signal, thanks to the “Metadata” and “Annotations” submenus which provide the following features.
Recompute#
The “Recompute” action allows you to recompute the selected signal(s) using
their original processing parameters. This is useful when you want to re-execute the
processing chain that was used to create a signal, for example after modifying global
settings or dependencies.
Note
This action is only available for signals that were created through processing operations and have stored processing parameters.
Select source objects#
The “Select source objects” action allows you to select the source
object(s) that were used to create the currently selected signal. This helps trace
back the processing history and understand which original signals were used as input
for the current result.
Note
This action is only available when exactly one signal is selected and that signal has source object references.
Metadata#
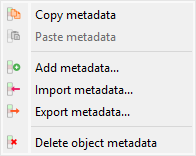
Screenshot of the “Metadata” submenu.#
Copy/paste metadata#
As metadata contains useful information about the signal, it can be copied and pasted
from one signal to another by selecting the “Copy metadata” and
“Paste metadata”
actions in the “Edit” menu.
This feature allows you to tranfer those information from one signal to another:
Regions Of Interest (ROIs): that is a very efficient way to reuse the same ROI on different signals and easily compare the results of the analysis on those signals
Analyze results, such as peak positions or FHWM intervals (the relevance of transferring such information depends on the context and is up to the user to decide)
Any other information that you may have added to the metadata of a signal
Note
Copying metadata from a signal to another will overwrite the metadata of the destination signal (for the metadata keys that are common to both signals) or simply add the metadata keys that are not present in the destination signal.
Import/export metadata#
Metadata can also be imported and exported from/to a JSON file using the “Import
metadata” and “Export metadata”
actions in the
“Edit” menu. This is exactly the same as the copy/paste metadata feature (see above
for more details on the use cases of this feature), but it allows you to save the
metadata to a file and then import it back later.
Delete metadata#
When deleting metadata using the “Delete metadata” action in the
“Edit” menu, you will be prompted to confirm the deletion of Region of Interests (ROIs)
if they are present in the metadata. After this eventual confirmation, the metadata
will be deleted, meaning that analysis results, ROIs, and any other information
associated with the signal will be lost.
Add metadata#
The “Add metadata” action allows you to add custom metadata items to
one or more selected signals. This is useful for tagging signals with experiment IDs,
sample names, processing steps, or any other custom information.
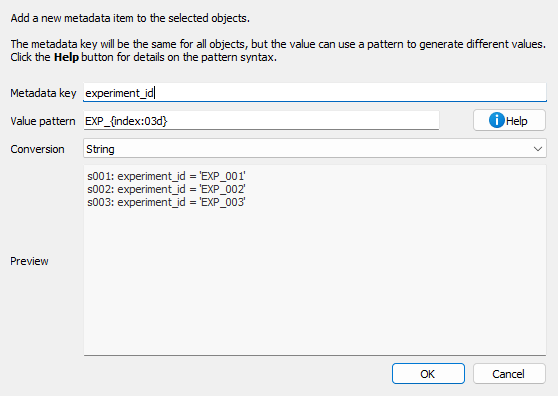
Add metadata dialog.#
When you select “Add metadata…” from the Edit menu, a dialog appears where you can:
Metadata key: Enter the name of the metadata field to add
Value pattern: Define a pattern for the metadata value using Python format strings
Conversion: Choose how to store the value (string, float, integer, or boolean)
Preview: See how the metadata will be added to each selected signal
The value pattern supports the following placeholders:
{title}: Signal title{index}: 1-based index of the signal in the selection{count}: Total number of selected signals{xlabel},{xunit},{ylabel},{yunit}: Axis labels and units{metadata[key]}: Access existing metadata values
You can also use format modifiers:
{title:upper}: Convert to uppercase{title:lower}: Convert to lowercase{index:03d}: Format as 3-digit number with leading zeros
Examples:
Add experiment ID: key=``experiment_id``, pattern=``EXP_{index:03d}``, conversion=string → Creates metadata like
experiment_id="EXP_001"Add sample temperature: key=``temperature``, pattern=``{metadata[temp]}``, conversion=float → Copies temperature from existing metadata and converts to float
Mark processed signals: key=``is_processed``, pattern=``true``, conversion=bool → Sets
is_processed=Truefor all selected signals
Annotations#
Annotations are visual elements that can be added to signals to highlight specific features, mark regions of interest, or add explanatory notes. DataLab provides a dedicated submenu in the “Edit” menu for managing annotations.
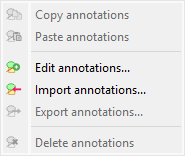
Screenshot of the “Annotations” submenu.#
Copy/paste annotations#
Annotations can be copied from one signal and pasted to one or more other signals
using the “Copy annotations” and “Paste annotations”
actions. This is useful when you want to apply the same visual markers across multiple
signals.
The “Paste annotations” action is only enabled when there are annotations in the clipboard (i.e., after using “Copy annotations”).
Edit annotations#
The “Edit annotations” action opens a dialog where you can view,
add, modify, or remove annotations from the current signal. This provides a visual
way to manage all annotations on a signal.
Import/export annotations#
Annotations can be saved to and loaded from JSON files (.dlabann extension) using
the “Import annotations” and “Export annotations”
actions. This allows you to:
Save annotation sets for later reuse
Share annotations with colleagues
Archive annotations separately from signal data
Apply the same annotations to different signals across sessions
The “Export annotations” action is only available when the selected signal has annotations.
Delete annotations#
The “Delete annotations” action removes all annotations from the
selected signal(s). This action is only enabled when the selected signal(s) have
annotations.
Note
Annotations are stored separately from metadata and analysis results. Deleting annotations does not affect ROIs or other metadata items.
Signal titles#
Signal titles may be considered as metadata from a user point of view, even if they are not stored in the metadata of the signal (but in an attribute of the signal object).
The “Edit” menu allows you to:
“Add object title to plot”: this action will add a label on top of the signal with its title.
“Copy titles to clipboard”
: this action will copy the titles of the selected signals to the clipboard, which might be useful to paste them in a text editor or in a spreadsheet.
Example of the content of the clipboard:
g001: s001: lorentz(a=1,sigma=1,mu=0,ymin=0) s002: derivative(s001) s003: wiener(s002) g002: derivative(g001) s004: derivative(s001) s005: derivative(s002) s006: derivative(s003) g003: fft(g002) s007: fft(s004) s008: fft(s005) s009: fft(s006)