Installation#
Quick install on Windows
Direct download link for the latest version of DataLab:
Warning
Important notice for users upgrading from DataLab v0.20 or earlier:
DataLab v1.0 introduces breaking changes that are not backward compatible with v0.20.
Plugins developed for v0.20 must be updated to work with v1.0
API changes affect custom code integrations
For detailed migration information, see the migration guide.
This section provides information on how to install DataLab on your system.
Once installed, you can start DataLab by running the datalab command in a terminal,
or by clicking on the DataLab shortcut in the Start menu (on Windows).
See also
For more details on how to execute DataLab and its command-line options, see Command line features.
For installation on systems without internet access, see the offline installation guide.
How to install#
DataLab is available in several forms:
As a Conda package.
As a Python package, which can be installed using the Package manager pip.
Windows As a stand-alone application, which does not require any Python distribution to be installed. Just run the All-in-one installer and you’re good to go!
Windows Within a ready-to-use Python distribution, based on WinPython.
As a precompiled Wheel package, which can be installed using
pip.As a Source package, which can be installed using
pipor manually.
See also
Impatient to try the next version of DataLab? You can also install the latest development version of DataLab from the master branch of the Git repository. See Development version for more information.
Conda package#
GNU/Linux Windows macOS
To install datalab package from the conda-forge channel (https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/datalab), run the following command:
$ conda install conda-forge::datalab
Package manager pip#
GNU/Linux Windows macOS
DataLab’s package datalab-platform is available on the Python Package Index (PyPI)
on the following URL: https://pypi.python.org/pypi/datalab-platform.
Installing DataLab from PyPI with Qt is as simple as running this command
(you may need to use pip3 instead of pip on some systems):
$ pip install datalab-platform[qt]
Or, if you prefer, you can install DataLab without the Qt library (not recommended):
$ pip install datalab-platform
Note
If you already have a previous version of DataLab installed, you can
upgrade it by running the same command with the --upgrade option:
$ pip install --upgrade datalab-platform[qt]
All-in-one installer#
Windows
DataLab is available as a stand-alone application for Windows, which does not require any Python distribution to be installed. Just run the installer and you’re good to go!
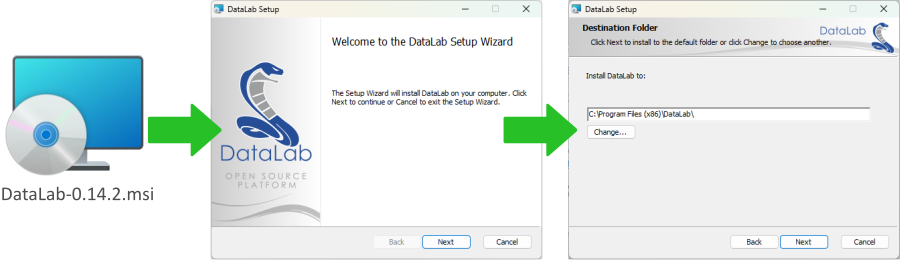
DataLab all-in-one installer for Windows#
The installer package is available in the Releases section. It supports automatic uninstall and upgrade feature (no need to uninstall DataLab before runinng the installer of another version of the application).
Warning
DataLab Windows installer is available for Windows 7 SP1, 8, 10 and 11.
On Windows 7 SP1, before running DataLab (or any other Python 3 application), you must install Microsoft Update KB2533623 (Windows6.1-KB2533623-x64.msu) and also may need to install Microsoft Visual C++ 2015-2022 Redistribuable package.
Python distribution#
Windows
DataLab is also available within a ready-to-use Python distribution, based on WinPython. This distribution is called DataLab-WinPython and is available in the DataLab-WinPython Releases section.

DataLab-WinPython is a ready-to-use Python distribution including the DataLab platform.#
The main difference with the all-in-one installer is that you can use the Python distribution for other purposes than running DataLab, and you may also extend it with additional packages. On the downside, it is also much bigger than the all-in-one installer because it includes a full Python distribution.
Note
DataLab-WinPython includes Spyder, a powerful IDE for scientific programming in Python, as well as Jupyter Notebook for interactive computing.
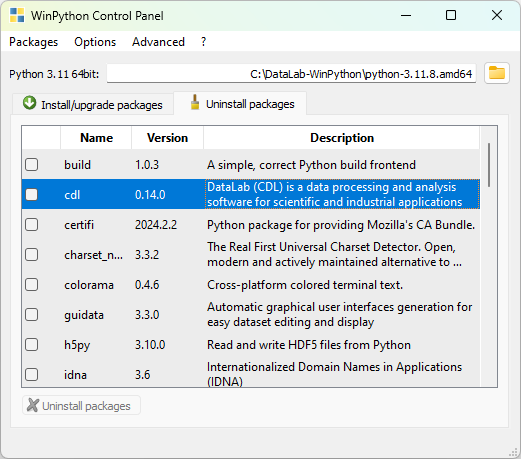
DataLab-WinPython Control Panel#
Warning
Whereas the all-in-one installer provides a monolithic package that guarantees the compatibility of all its components because it cannot be modified by the user, the WinPython distribution is more flexible and thus can be broken by a bad manipulation of the Python distribution by the user. This should be taken into account when choosing the installation method.
Wheel package#
GNU/Linux Windows macOS
On any operating system, using pip and the Wheel package is the easiest way to install DataLab on an existing Python distribution:
$ pip install --upgrade DataLab-1.0.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl
Source package#
GNU/Linux Windows macOS
Installing DataLab directly from the source package may be done using pip:
$ pip install --upgrade datalab-1.0.1.tar.gz
Or, if you prefer, you can install it manually by running the following command from the root directory of the source package:
$ pip install --upgrade .
Finally, you can also build your own Wheel package and install it using pip,
by running the following command from the root directory of the source package
(this requires the build and wheel packages to be installed):
$ pip install build wheel # Install build and wheel packages (if needed)
$ python -m build # Build the wheel package
$ pip install --upgrade dist/datalab-1.0.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl # Install the wheel package
Development version#
GNU/Linux Windows macOS
If you want to try the latest development version of DataLab, you can install it directly from the master branch of the Git repository.
The first time you install DataLab from the Git repository, enter the following command:
$ pip install git+https://github.com/DataLab-Platform/DataLab.git
Then, if at some point you want to upgrade to the latest version of DataLab, just run the same command with options to force the reinstall of the package without handling dependencies (because it would reinstall all dependencies):
$ pip install --force-reinstall --no-deps git+https://github.com/DataLab-Platform/DataLab.git
Note
If dependencies have changed, you may need to execute the same command as above,
but without the --no-deps option.
Dependencies#
Note
The DataLab all-in-one installer already include all those required libraries as well as Python itself.
The datalab-platform package requires the following Python modules:
Name |
Version |
Summary |
|---|---|---|
Python |
>=3.9, <4 |
Python programming language |
guidata |
>= 3.13.4 |
Automatic GUI generation for easy dataset editing and display |
PlotPy |
>= 2.8.2 |
Curve and image plotting tools for Python/Qt applications |
Sigima |
>= 1.1.0 |
Scientific computing engine for 1D signals and 2D images, part of the DataLab open-source platform. |
NumPy |
>= 1.22, < 2.5 |
Fundamental package for array computing in Python |
SciPy |
>= 1.10.1, < 1.17 |
Fundamental algorithms for scientific computing in Python |
scikit-image |
>= 0.19.2, < 0.27 |
Image processing in Python |
pandas |
>= 1.4, < 3.0 |
Powerful data structures for data analysis, time series, and statistics |
PyWavelets |
>= 1.2, < 2.0 |
PyWavelets, wavelet transform module |
psutil |
>= 5.8 |
Cross-platform lib for process and system monitoring. |
packaging |
>= 21.3 |
Core utilities for Python packages |
fastapi |
>= 0.110.0 |
FastAPI framework, high performance, easy to learn, fast to code, ready for production |
uvicorn[standard] |
>= 0.27.0 |
|
pydantic |
>= 2.0 |
Data validation using Python type hints |
Optional modules for GUI support (Qt):
Name |
Version |
Summary |
|---|---|---|
PyQt5 |
>= 5.15.6 |
Python bindings for the Qt cross platform application toolkit |
Optional modules for development:
Name |
Version |
Summary |
|---|---|---|
build |
A simple, correct Python build frontend |
|
babel |
Internationalization utilities |
|
Coverage |
Code coverage measurement for Python |
|
pylint |
python code static checker |
|
ruff |
An extremely fast Python linter and code formatter, written in Rust. |
|
pre-commit |
A framework for managing and maintaining multi-language pre-commit hooks. |
Optional modules for building the documentation:
Name |
Version |
Summary |
|---|---|---|
sphinx |
Python documentation generator |
|
sphinx_intl |
Sphinx utility that make it easy to translate and to apply translation. |
|
sphinx-sitemap |
Sitemap generator for Sphinx |
|
myst_parser |
An extended [CommonMark](https://spec.commonmark.org/) compliant parser, |
|
sphinx_design |
A sphinx extension for designing beautiful, view size responsive web components. |
|
sphinx-copybutton |
Add a copy button to each of your code cells. |
|
pydata-sphinx-theme |
Bootstrap-based Sphinx theme from the PyData community |
Optional modules for running test suite:
Name |
Version |
Summary |
|---|---|---|
pytest |
pytest: simple powerful testing with Python |
|
pytest-xvfb |
A pytest plugin to run Xvfb (or Xephyr/Xvnc) for tests. |
|
httpx |
The next generation HTTP client. |
Note
Python 3.11 and PyQt5 are the reference for production release